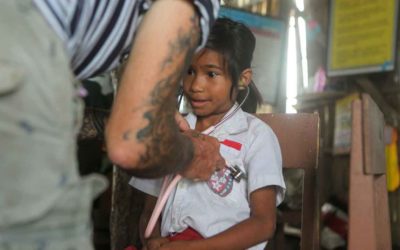Discover how the East Sumba Malaria Prevention Initiative we are presently executing is combatting this destructive ailment. By implementing preventive measures like distributing mosquito nets treated with insecticides and raising awareness on eliminating mosquito breeding sites, this initiative strives to diminish the occurrence of malaria in the area. Witness the combined efforts of Fair Future and Kawan Baik, working together with local authorities and the severely impacted ultra-rural communities, to safeguard the population against this mosquito-transmitted disease.
To reach ultra-rural villages, we rely on the Truck of Life to navigate rough, broken roads. This vehicle allows us to deliver essential supplies, including medicines, water, tools, solar kits, and food. Logistics play a crucial role in our program; without access to fuel, spare parts, and the commitment to long days on the road, we would be unable to reach the patients in need.
Donate
Support Care
Programs
All projects
Quick News
Field updates
Stories
Field stories
Fair Future’s mission: to provide basic medical care and treatment in areas with no healthcare infrastructure.
Behavioral Impacts on Spread of Malaria
Beyond Borders: Fighting Malaria Together in Eastern Indonesia. This new "Picture of the Day" shows a young girl from Lapinu village who appears unwell. Taken in 2020, Alex examined her and used a stethoscope to listen to her heartbeat. In April 2023, we revisited the village as part of the Primary Medical Care program. Unfortunately, the girl contracted malaria and suffered from high fever, body pains, and poor overall health. However, after receiving treatment and giving advice to her mother, the little girl has shown significant improvement after just one month.
Our organisation is dedicated to promoting public health in ultra-rural regions of Indonesia (like here in East Sumba), and we're deeply concerned about the impact of malaria on vulnerable communities, as you know already. Sadly, malaria remains a leading cause of illness and death in Indonesia, particularly in East Sumba, where we are based.
Some little history: The word "malaria" originates in Italian. It comes from the expression "mal'aria", which translates as "bad air". This term was used historically to describe the belief that disease was caused by inhaling polluted or stale air in swampy areas. The Plasmodium parasite is responsible for causing malaria, and research suggests that it has been affecting humans for at least 4,000 years.
Several human behaviours contribute irreparably to the spread or persistence of malaria. Here are some of the factors that lead to an increase in malaria cases:
Failure to prevent mosquito bites, poor waste management, inadequate housing and sanitation, deterioration of hygienic conditions, deforestation, alterations to natural habitats, movement of people, drug resistance*** and misuse, limited access to health services, higher illiteracy rates among younger populations, and lack of community involvement and awareness can all lead to an increase in malaria cases… And this, among other examples!
As a result, many people, particularly children and pregnant women, continue to suffer from this preventable and treatable disease. Our program aims to tackle these issues head-on by implementing various activities to strengthen malaria control efforts in the region. It is crucial to highlight that combatting malaria demands a unified strategy encompassing preventive and therapeutic measures. It also involves initiatives to enhance the environment and living standards of communities affected by the disease.
***The problem of self-medication and the consequent development of resistance to antimalarial drugs are two interconnected challenges that significantly hinder the effective management and control of malaria.
Our aim is to take swift action against malaria
Malaria has a significant impact on Eastern Indonesia, specifically Sumba Timur, due to its remote and inaccessible locations, insufficient healthcare infrastructure, and limited preventative measures. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria are both prevalent in these areas, with malaria transmission occurring year-round. We have partnered with various donors and organizations to take swift and efficient action to address this critical health issue.
Primary Medical Care Progress Report
The Primary Medical Care (PMC) program has made a remarkable difference in the rural communities of East Sumba, providing over a thousand treatments that offer critical medical assistance to those in need. Through their unwavering dedication and hard work, the women of the region have been empowered to take control of the health and welfare of their ultra-rural communities. By providing them with the essential knowledge, resources and tools, we have successfully equipped them to face all the socio-medical challenges that come their way. Over nearly five months, Fair Future and Kawan Baik, our partners, all participants, and teams collaborated to go above and beyond in reaching the most challenging areas and evaluating the impact of the field program. The results are awe-inspiring, leaving no doubt that the Primary Medical Care program is the definitive solution to ensure everyone can access emergency medical assistance.
Kullup is a hole in the rock to collect rainwater
This new "Picture of the Day" shows you kids from the village of Laidatang, who fetch water far from home in the "Kullup" of the village. Elthon, responsible for documentation (with the black t-shirt), and Alex, from the medical staff, are also present in this photo. With the kids and one or two adults accompanying us, we walk more than an hour to reach this place in the middle of a high hill. You must descend a steep path to access these hand-dug holes in the rock. In 30 minutes, we will have to go up the hill and walk back. But this time, loaded with several jerrycans filled to the brim.
The Fair Future and Kawan Baik teams spend two days with the families of the ultra-rural and isolated village of Laindatang to get to know them even better. In this village, we have the project to create a #WaterConnections project. I let you read here the articles related to this project and here to see what your want to do to save their lives,
In Laindatang, families only have access to rainwater. It's for everything: eating, drinking, cooking, bathing, washing clothes, drinking water, caring for children, sick people or watering animals. Therefore, one of the ways for women and young girls to have water at home to live on is to walk several kilometres to find the "Kullup".
Kullup, what is it? These are small stone basins, directly dug into the rock by the villagers, used to collect and store rainwater in rural areas. When it rains, the water seeps into the ground at the top of the hill and then is filtered through the earth and the basements. It flows drop by drop in these stone basins, the "Kullup". Then the villagers come to fill their jerrycans with five or ten litres.
The "Kuluk" are an essential water source for the local communities. But the quality of stored water can be affected by bacterial contamination, chemicals, animal waste or debris. Therefore, regularly cleaning these small holes in the rock is essential to maintain water quality. It is important to note that the "kuluk" is only a temporary solution to the water crisis in areas with limited access to drinking water. Indeed, the "kuluks" cannot fill up correctly without rain. They dry out about ten days after the last rains and remain dry for almost nine months. To find water, young girls, women and children, sometimes under five, will have to walk even further and longer.
Our two organizations work with local communities to implement longer-term solutions, such as constructing water supply networks using deep boreholes and sealed and healthy rainwater cisterns. The Water Connections program offers innovative and sustainable solutions. It includes promoting water conservation practices with “Kawan Sehat” and self-sustaining access to Primary Medical Care through the PMC program.
Helping ultra-rural families to have a healthier life
This new "Picture of the Day" features Kawan Ino, one of the Fair Future team members in Sumba (Rumah Kambera Leader), talking to health workers and the village community of Kabanda. To do this, he uses the "Kawan Sehat" book we produced at the end of 2022 for children in these regions. This book is an integral part of the program of access to primary medical care for children in ultra-rural areas.
We spend two days here, and you can read what we have done in Kabanda. This village is genuinely one of the most isolated I have ever seen. Getting it is difficult, even dangerous, at times. No road leads to this village; only extremely steep or steep stony paths allow us to go there. Kawan Ino explains how to have a healthier life thanks to implementing specific things in everyday life. This includes physical and mental health, body and home hygiene, daily habits and women empowerment.
Thanks to the Kawan Sehat program, we see a significant improvement in the health and well-being of rural populations. It is truly heartening to see healthy habits being encouraged and access to health care increasing. It is vital that everyone has access to quality health care, and we are happy that this program allows more people to receive the care they need.
Here, when a person is sick or injured while a woman is due to give birth, one of the only ways for her to receive medical attention is to carry her on people's backs for several hours or even a whole day until the nearest health centre. This person also does not know if he will arrive in time at the medical centre, called "Puskesmas or Pustu", as we have seen on several occasions.
This is why this book is necessary: “Kawan Sehat” is intended for schools and teachers. It's an amazing teaching aid for them, and kids love it. Nothing is done here to give children the means to learn from an early age how to wash themselves, eat healthier, use soap, and learn not to pollute or brush their teeth etc… In the classrooms here in East Sumba, the book“Kawan Sehat” is the only one available for children; there are no others.
Let’s prevent malaria rather than cure it!
In this "Picture of the Day" shows you three children from Kabanda Village in East Sumba (read this post here), where the PMC program is in place. In this village, very far from everything, especially health centres, malaria is very active and wreaking havoc. We are talking about 80% of children under 12 are affected. It is, therefore, essential to prevent and train families. This is what we are doing here.
The daily observations concerning the causes of malaria are multiple here. These include, in particular, the lack of access to health care, information on prevention methods, the unavailability of health centres and sanitation, and the growing resistance to antimalarial drugs for regions with access to these treatments.
A reminder for all Kawans: Malaria is transmitted by female mosquitoes of the "Genus Anopheles", throughout the East Sumba region. These mosquitoes breed in standing water, such as rainwater storage tanks and open water sources, most of the time in rural and deprived areas of East Sumba.
As Fair Future has repeatedly seen and repeated for years, the consequences of malaria are serious if nothing is done to treat it: High fever, severe headache, nausea and vomiting. If not treated quickly, the disease can progress and lead to severe complications, including kidney failure, anaemia, seizures and death.
It is essential to train families and rural communities to protect themselves from this disease to reduce its transmission. Also, by learning how to prevent and treat Malaria, rural families and communities will reduce the economic and social burden of the disease. Malaria entails high costs for families and communities, particularly medical expenses (if they can access them), school absenteeism, and reduced productivity.
As we apply it with the Primary Medical Care Program (PMC), training families and rural communities to protect themselves from malaria contributes to strengthening the resilience of these populations in the face of epidemics of infectious diseases such as HIV, Tuberculosis, Gastroenteritis, cholera etc…
Alexandre Wettstein from the Foundation’s Medico-Social Camp in East Sumba, Rumah Kambera, Lambanapu, on the 2nd of May 2023
Fighting Malaria in Eastern Indonesia
East Sumba, where we work at the time of writing this article, was experiencing a dramatic malaria epidemic. In the first quarter of 2023, there were more than 28,000 cases of Malaria, a significant increase from the previous year. A few months ago, Fair Future declared this life-threatening emergency. Despite our best efforts, Malaria cases are increasing. Here, when a child has a fever, it is more than 80% of the time a question of Malaria. We conduct health education campaigns to raise awareness of the importance of malaria prevention and early detection. Efforts to control the epidemic should include the distribution of mosquito nets, the provision of essential antimalarial drugs, as well as rapid diagnostic tests.
Medical care for children affected by Malaria
In this "Picture of the Day", Fair Future and Kawan Baik medical teams provide medical care to a child most likely affected by Malaria. He is less than two years old and has a fever of 40.6. Her symptoms fit this diagnosis of Malaria. We give him appropriate primary medical care to reduce his fever as quickly as possible. Then he will go for treatment tomorrow at the nearest health centre, more than three hours from the village.
Malaria is a severe public health problem, especially in the ultra-rural and impoverished areas where Fair Future and Kawan Baik Foundations work so hard. Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Children under five and pregnant women are also particularly vulnerable to Malaria, as their immune systems are less developed and may have more difficulty fighting infection. People suffering from chronic illnesses are also vulnerable (HIV, Hepatitis, malnutrition, etc.)
Ultra-rural and poor areas such as East Sumba are particularly vulnerable to the spread of Malaria due to factors such as lack of water or contaminated water, deplorable housing conditions, lack of access to healthcare health and preventive measures, inadequate sanitation… Moreover, here we do not have antimalarial drugs nor rapid tests to detect the disease. This makes our treatment and prevention work very difficult.
PMC program evaluation in Lapinu
These women linked to the PMC program devote part of their lives to saving others. These unsung heroines work tirelessly to keep people from the danger of illness and injury. They put their lives on the line to ensure others can live to see another day. Teachers trained in primary medical care, these women are the backbone of these ultra-rural communities in East Sumba. They exemplify true bravery and selflessness, and we are eternally grateful for their service. Therefore, we express our deep gratitude to all women who save lives. Thanks for what you’re doing for the others.
PMC program evaluation in Kabanda
Kabanda is genuinely one of the most isolated I have ever seen. Getting it is difficult, even dangerous, at times. No road leads to this village; only extremely steep or steep stony paths allow us to go there. It took us over six hours to get there, including four hours of absolute terrain with the Truck of Life, a 4×4 medical truck specially designed for this journey. Kabanda is no exception; so many villages are in the same situation: That is to say, they have no road leading there. This raises – among other things – the question of access to health care, of course. And it is for these types of communities that Fair Future exists, and together with our friends from Kawan Baik, Sumba Volunteer and Charis Foundation, we have created this primary medical care program.
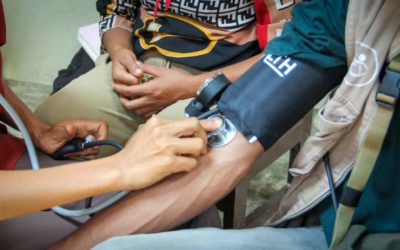
Check blood pressure in rural areas
Here in the ultra-rural and poor areas where Fair Future Foundation and Kawan Baik Indonesia work, populations tend to have a higher prevalence of high blood pressure than in urban and wealthier areas. This is mainly due to poor diet, excessive tobacco consumption, and poor hydration. Of course, poverty and limited access to resources will also contribute to higher stress levels, increasing blood pressure. An unhealthy lifestyle increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and other health problems. We teach some “Kawan Sehat” health workers participating in the primary medical care program to measure blood pressure and take the necessary measures.